With $1M+ hourly downtime costs at stake, semiconductor OEMs need a deployment roadmap that delivers fast ROI without disrupting fab operations.
Deploy AI in field service by integrating telemetry from lithography and etch tools into technician dispatch systems. Start with chamber kit prediction to reduce repeat visits, then expand to recipe drift detection and contamination tracing as data quality improves.
Lithography, etch, and deposition equipment from different vendors generate incompatible data formats. Technicians lack unified visibility into failure patterns across tool types, forcing reactive maintenance instead of predictive intervention.
Process engineers with decades of chamber optimization knowledge are retiring. Their expertise in correlating recipe drift with component wear exists only in notebooks and memory, not in systems accessible to newer technicians.
Connecting AI models to existing field service management platforms requires custom APIs and data pipelines. Leadership fears deployment delays and disruptions to fab schedules that already operate at 95%+ equipment availability targets.
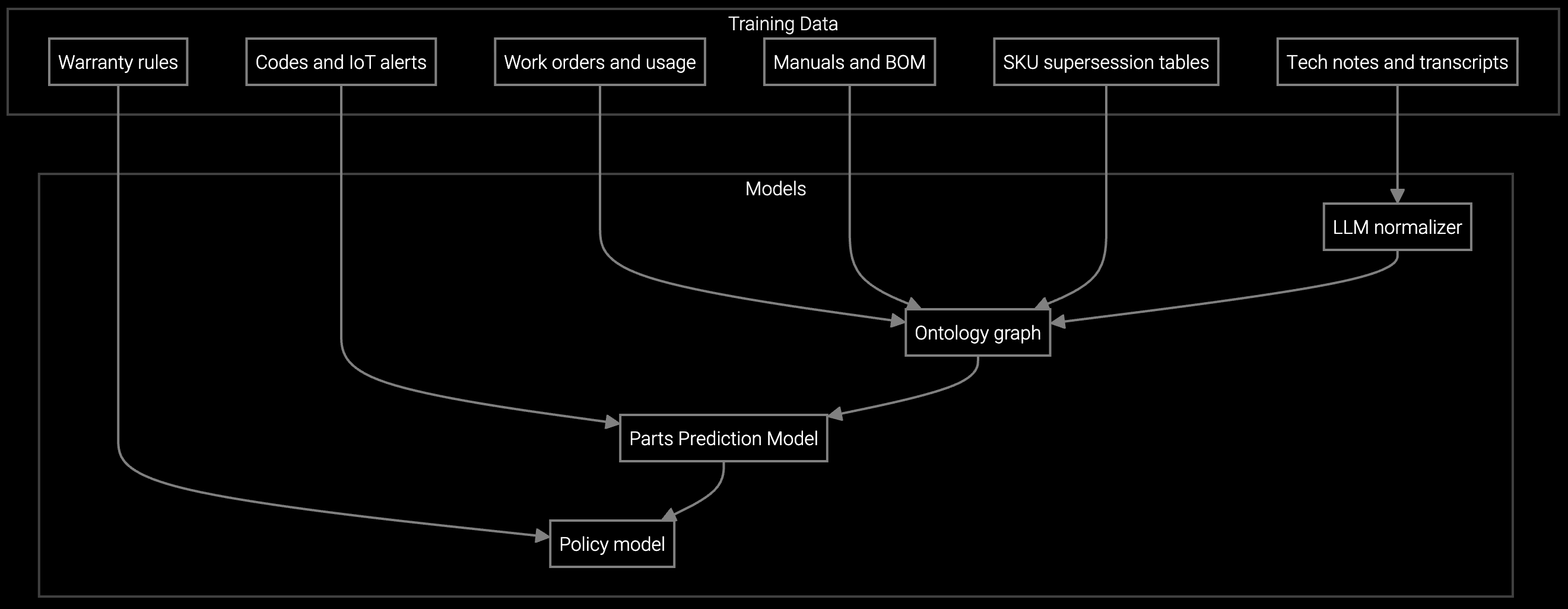
Successful AI deployment in semiconductor field service follows a three-phase approach that minimizes risk while demonstrating value quickly. Phase one connects equipment telemetry to parts prediction models for high-wear components like chamber kits and RF generators. The platform ingests sensor data from existing fab automation systems without requiring tool downtime, building predictive models that alert technicians 48-72 hours before component failure.
Phase two extends AI capabilities to on-site diagnostics by deploying mobile copilot tools that surface historical failure patterns and tribal knowledge captured from retiring engineers. Technicians arriving at a down EUV lithography tool receive real-time guidance on symptom correlation, contamination sources, and recipe parameter verification. Phase three closes the loop by automating work order creation from anomaly detection, routing high-complexity issues to specialist engineers while standard chamber replacements flow directly to dispatch.
Predict chamber kit and consumable failures for lithography and etch tools, ensuring technicians arrive with correct parts to minimize fab downtime and protect wafer throughput.
Correlate recipe drift symptoms with historical contamination patterns and process engineer expertise to identify root causes in EUV and DUV lithography systems faster.
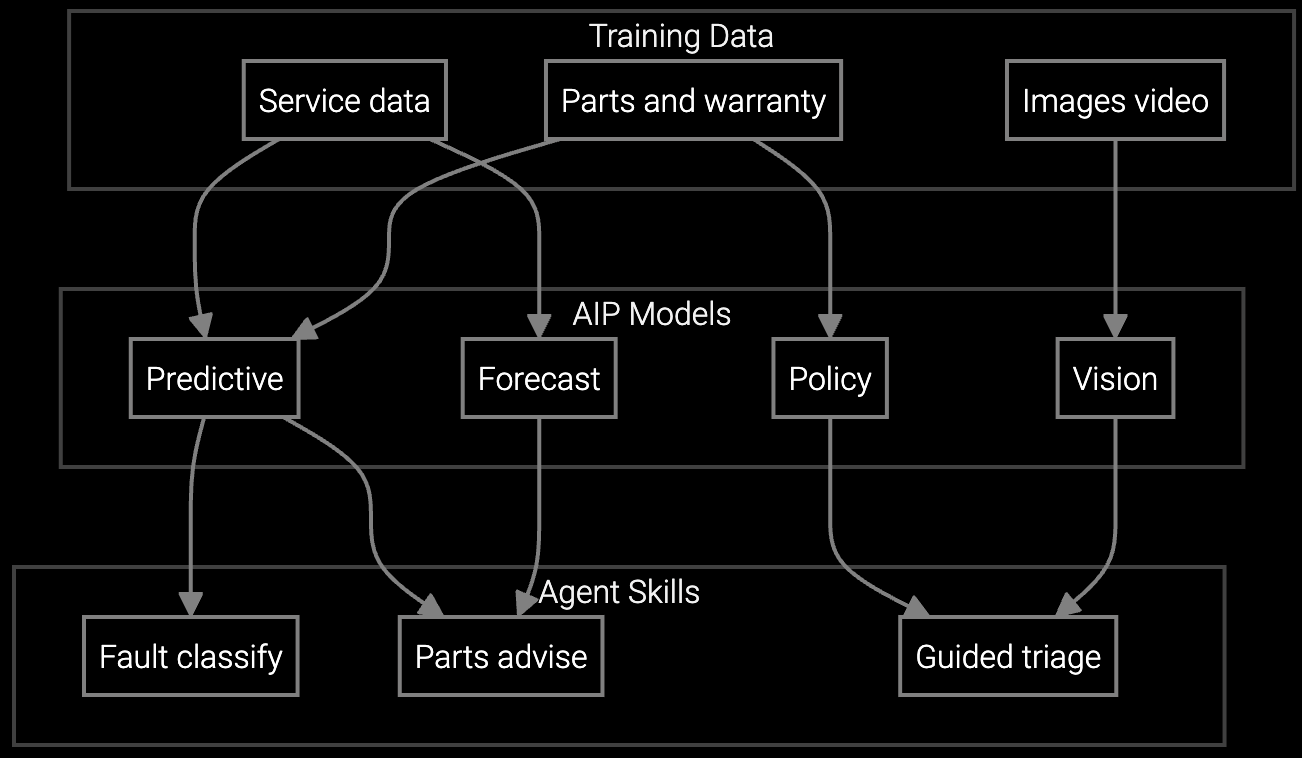
Mobile AI copilot provides real-time guidance on chamber diagnostics, recipe parameter verification, and contamination source tracing for on-site technicians at fab equipment.
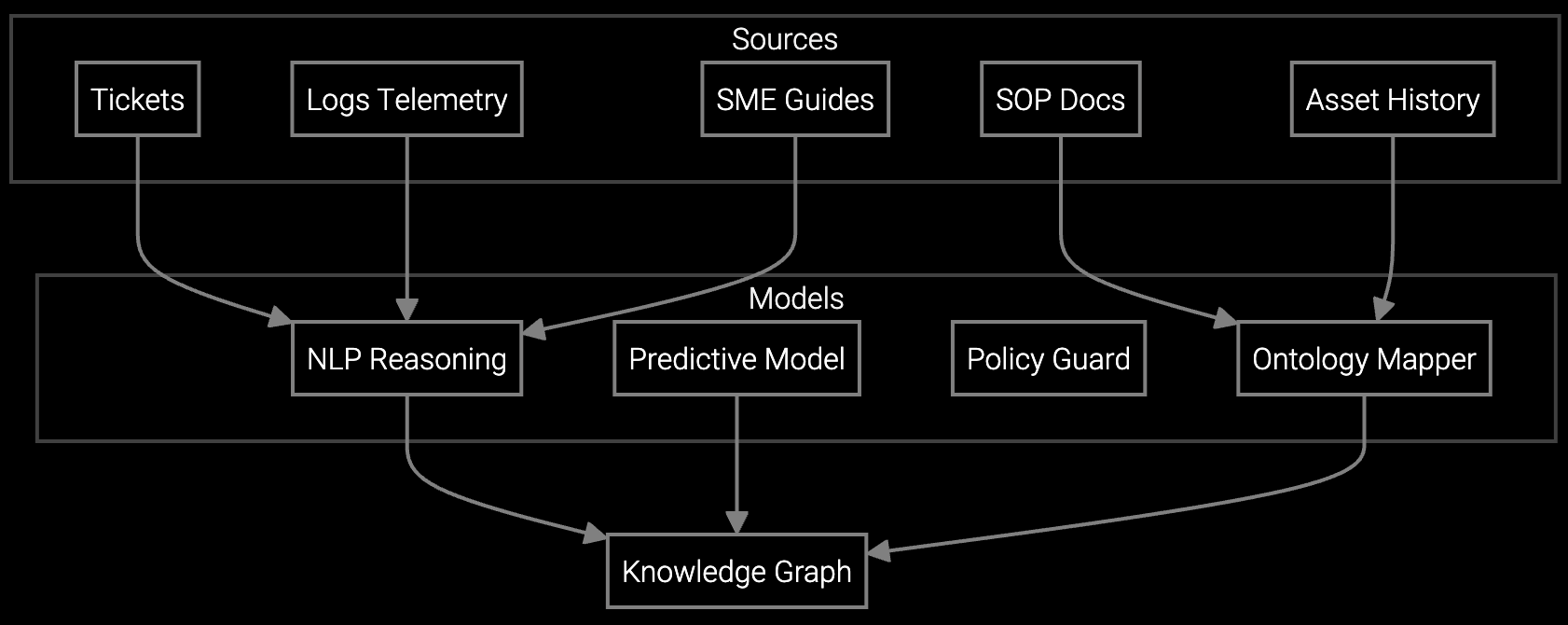
Semiconductor fabs operate at equipment availability targets exceeding 95%, making any deployment that risks tool downtime unacceptable. The platform connects to existing fab automation systems and MES infrastructure via read-only data feeds, eliminating integration risk. Initial deployment focuses on high-wear tools like plasma etch chambers and CVD reactors where parts prediction delivers immediate ROI through reduced unplanned downtime.
Process engineers train AI models using historical PM records, recipe parameters, and sensor logs from FOUP handling and metrology equipment. The system learns correlations between chamber component wear and process drift indicators like etch rate uniformity or deposition thickness variation. As model accuracy improves, coverage expands to lithography tools and implant systems where downtime costs exceed $1M per hour.
The platform ingests equipment telemetry from fab automation systems, including sensor logs from etch chambers, lithography tools, and deposition equipment. It also uses historical PM records, work order data from FSM systems, recipe parameters from process control databases, and parts consumption tracking. Read-only API connections prevent any risk to production tool operation during integration.
Phase one deployment targeting chamber kit prediction for 50-100 tools completes in 8-12 weeks. This includes API integration with existing MES and FSM systems, historical data ingestion from the past 12-18 months, initial model training, and validation against known failure events. Technician mobile tool deployment and knowledge capture workflows add another 4-6 weeks in phase two.
Prioritize plasma etch chambers and CVD reactors because they have the highest parts replacement frequency and clearest correlation between sensor data and component failure. These tools generate 60-70% of unplanned field service visits in most fabs, making them ideal for demonstrating FTF rate improvement and truck roll cost reduction within the first quarter post-deployment.
Engineers document their diagnostic reasoning by annotating historical failure cases through a guided workflow interface. The platform extracts patterns linking symptoms like recipe drift or yield degradation to root causes such as contamination sources or worn chamber components. This expertise becomes searchable and surfaces automatically when technicians encounter similar failure signatures on-site.
OEMs typically achieve 15-25% reduction in truck roll costs within six months through improved FTF rates and better parts pre-staging. For a fab running 200+ tools, this translates to $2-4M annual savings from reduced emergency dispatch and faster MTTR. Additional margin protection comes from avoiding SLA penalties when contamination or recipe drift issues are caught proactively before customer yield impact.

How AI bridges the knowledge gap as experienced technicians retire.

Generative AI solutions for preserving institutional knowledge.

AI-powered parts prediction for higher FTFR.
See how Bruviti's phased deployment approach protects fab uptime while delivering measurable FTF and cost improvements.
Schedule Implementation Review