Network Incident Management
AI-powered L1/L2 triage automation for SD-WAN and SASE environments that auto-triages ≥70% of recurring connectivity tickets, resolves ≥50% at L1/L2, and cuts MTTR by ≥40%.
Challenge
Support teams handle a high volume of recurring SD-WAN connectivity and performance tickets in mixed SD-WAN and SASE environments. Tooling and ownership are siloed across controllers, security stacks, and DDI platforms, so L1/L2 agents rely on tribal knowledge, manual log scraping, and frequent L3 escalations. Repeat offenders include DNS reachability and slowness, policy changes that block traffic, HA failover blocked by configuration drift, missing VLANs on trunks, DHCP scope mismatches, and STP misconfigurations—driving long MTTR and service disruption.
The objective: Auto-triage ≥70% of recurring SD-WAN tickets and resolve ≥50% at L1/L2; cut MTTR by ≥40%; reduce L3 escalations by ≥35%, with compliant updates to ITSM, CMDB, and controller audit logs.
Solution: How AIP changed the operating model
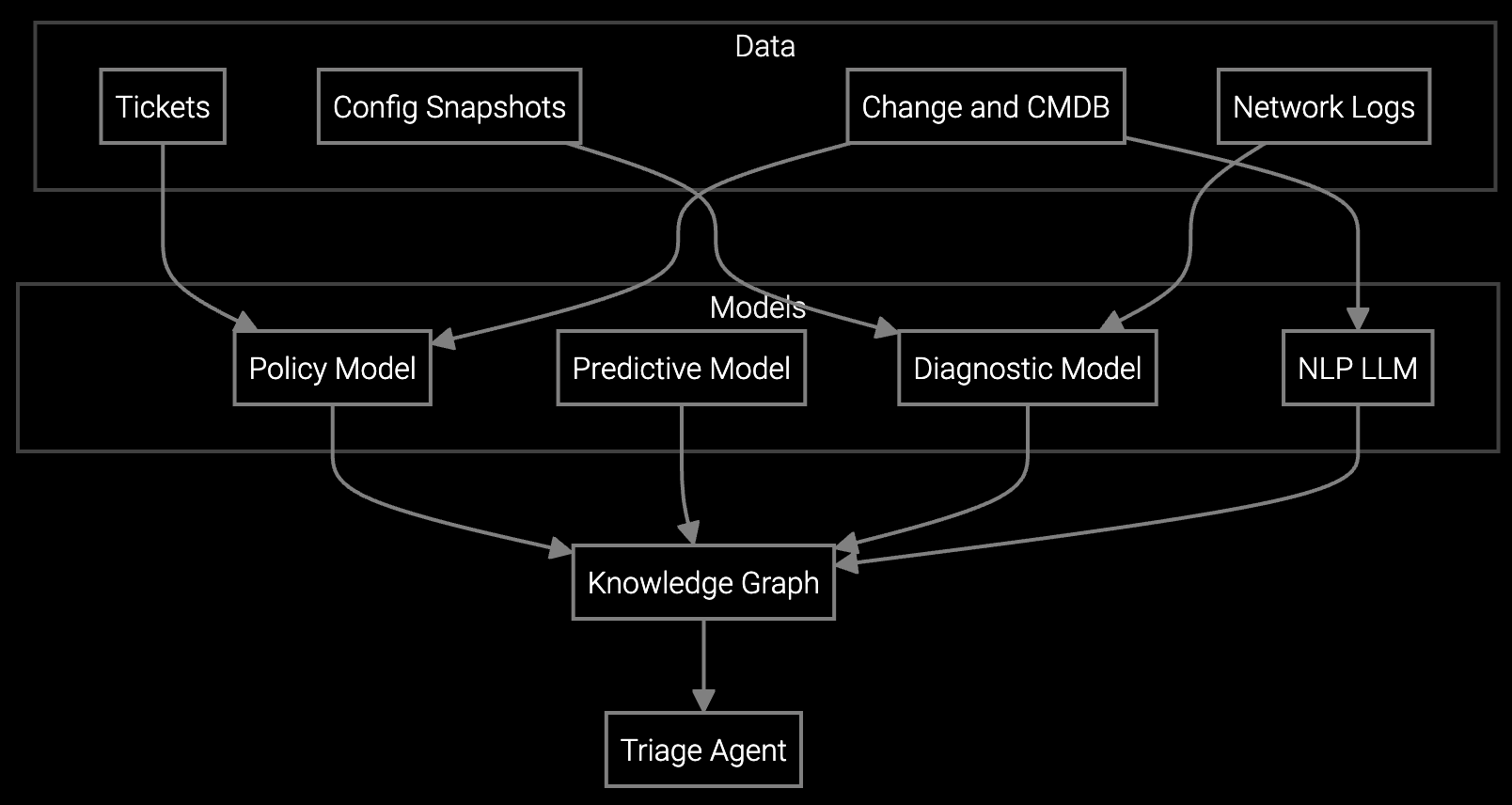
Learning and setup
Powered by the Aftermarket Intelligence Platform (AIP), the agentic solution applied its predictive, policy, diagnostic, and NLP models backed by an ontology-driven knowledge graph. Training data came from historical tickets and resolutions, device configuration snapshots, SD-WAN and SASE logs and telemetry, provisioning and change history, troubleshooting guides and SME notes, CMDB, and feedback from resolved cases. This enabled the AI agent to recognize and interpret device and site IDs, circuit and carrier IDs, link health metrics, DNS and DHCP data, policy versions and diffs, VLAN IDs and trunk state, HA status, STP state, syslogs, NetFlow, change tickets, maintenance windows, and severity.
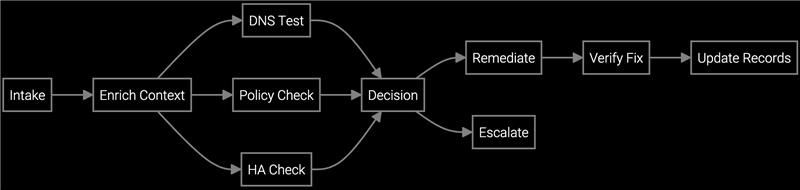
Workflow orchestration
The AI agent reads new or updated tickets from ITSM, extracts identifiers, and selects the path to test DNS, inspect policy drift, validate routes, and confirm HA readiness, VLAN and DHCP health, and STP stability. It navigates SD-WAN controllers, SASE consoles, DDI platforms, SIEM and log stores, mirroring the steps a seasoned network engineer would take. Orchestration logic branches—for example, if policy version drift or change outside a maintenance window is detected, the agent prioritizes rollback or opens a gated change—while enforcing guardrails and auditability.
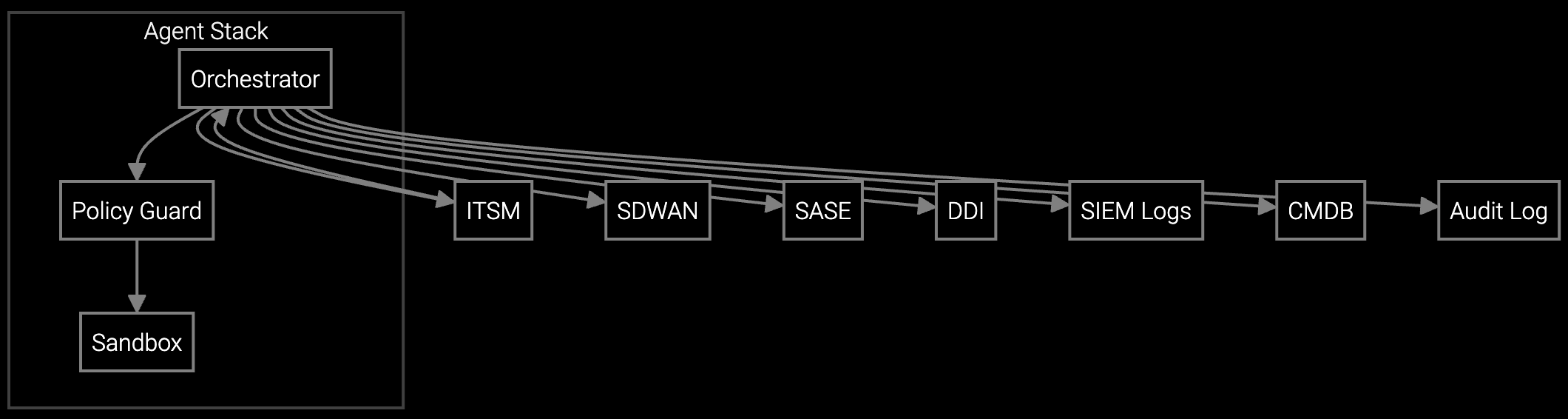
Execution and resolution
The AI agent correlates recent changes with symptoms, runs DNS reachability and latency tests, validates security rules and route maps, detects VLAN, DHCP, and STP inconsistencies, and checks HA failover readiness. It proposes ranked root causes with confidence, generates guided playbooks for L1/L2, and auto-executes safe remediations behind guardrails—such as policy rollback, DHCP scope fix, or VLAN tagging—after impact simulation and approvals when required. Responses complete in minutes, with evidence posted to ITSM, CMDB, and controller audit logs. Exceptions—such as multi-domain outages, missing telemetry, or conflicting policies—are routed to support engineers with structured summaries and next best actions attached.