Senior technicians are retiring with decades of equipment knowledge while service costs erode margins.
AI orchestrates dispatch-to-resolution workflows for industrial equipment service, automating triage, parts pre-staging, technician routing, and job documentation—eliminating manual handoffs while preserving expertise from retiring field engineers.
Technicians arrive without the right parts or complete equipment history. Second and third truck rolls compound labor costs and erode customer trust in OEM service capability.
Veteran technicians retire with undocumented knowledge of legacy industrial equipment spanning 20-30 year lifecycles. Junior technicians lack guidance on complex diagnostics for older machinery still under contract.
Technicians spend billable hours documenting work orders, uploading photos, categorizing failure codes, and requesting parts—reducing actual wrench time and increasing service delivery costs.
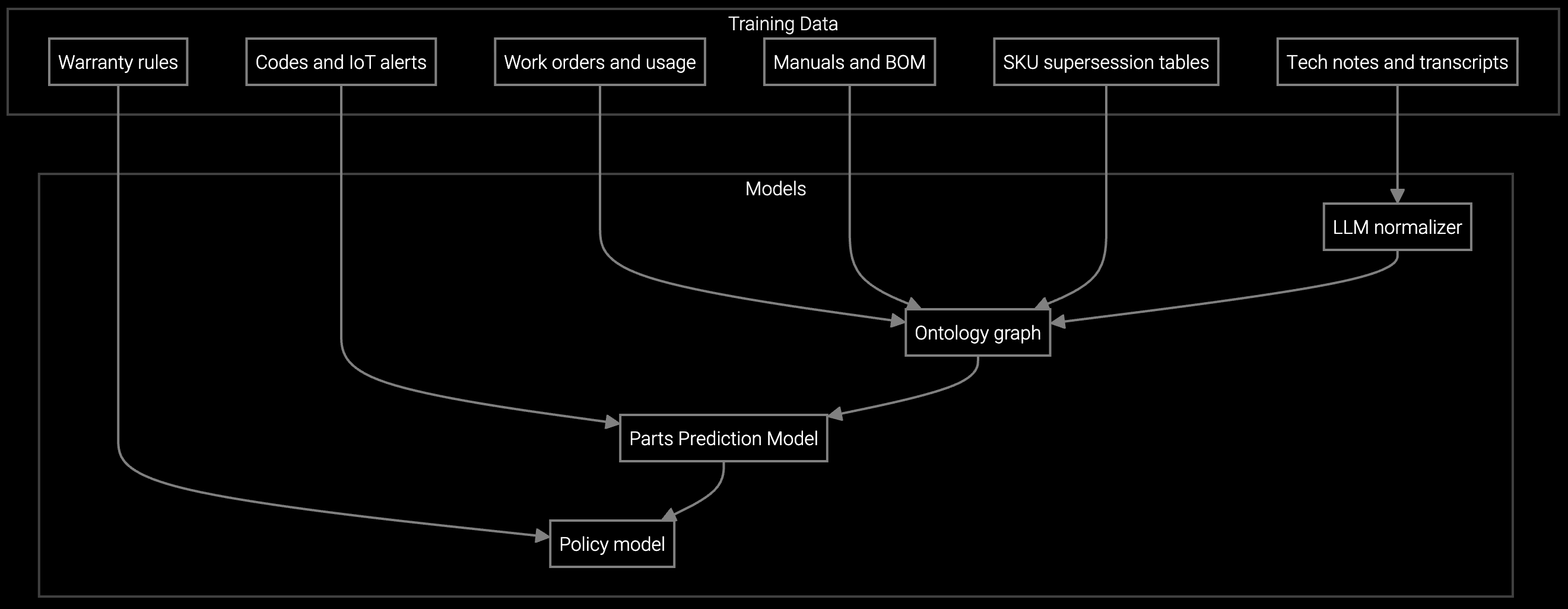
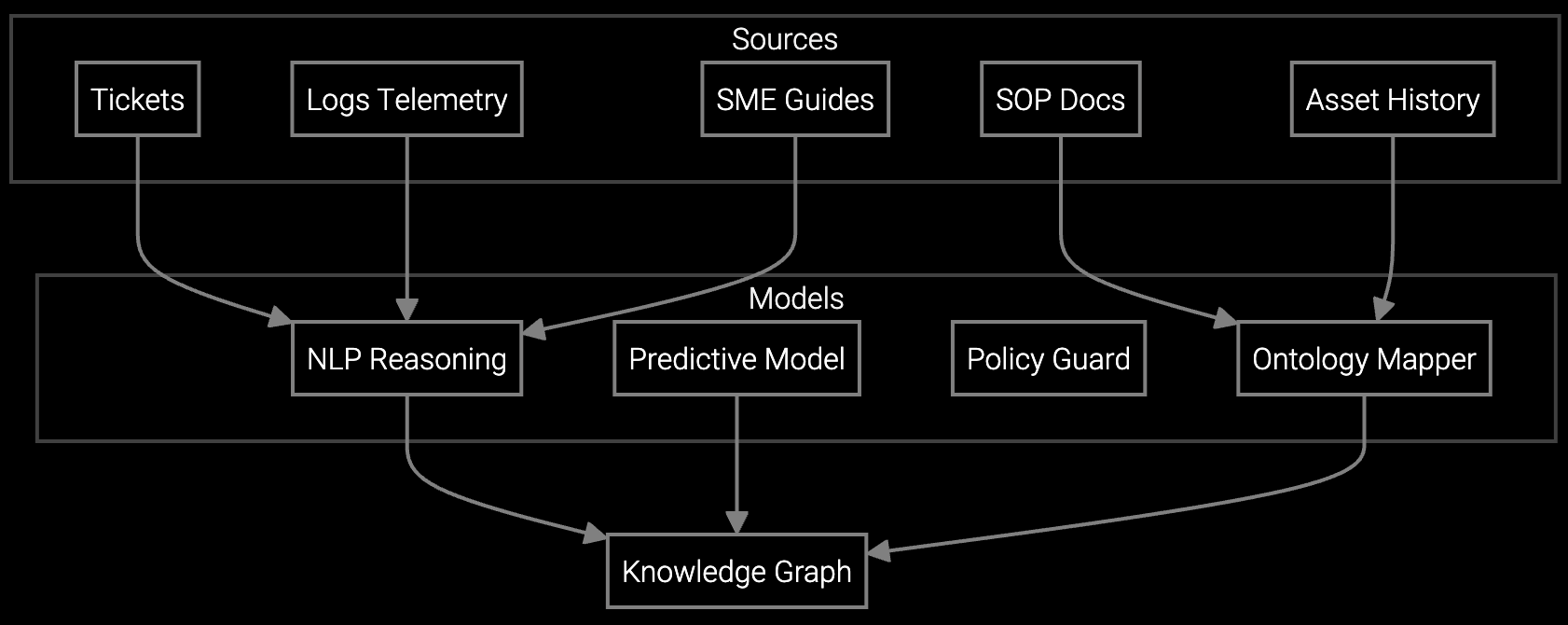
The platform connects SCADA telemetry, equipment history, parts inventory, and field service management systems into a unified workflow engine. When a failure event occurs, AI analyzes sensor patterns against historical data to predict root cause, pre-stage required parts at the nearest depot, and route the optimal technician based on expertise match and location—before a work order is manually created.
On-site, technicians access a mobile copilot that provides step-by-step repair procedures drawn from decades of tribal knowledge now encoded in the AI. The system auto-fills job documentation, categorizes failure codes, orders replacement parts, and updates the digital twin—transforming post-job administration from a 45-minute manual task to a zero-touch process. Service leaders gain real-time visibility into first-time fix trends and technician utilization without chasing spreadsheets.
Predicts which industrial equipment parts technicians will need before dispatch, analyzing equipment age, failure symptoms, and historical repair patterns to improve first-time fix rates.
Correlates PLC sensor data and failure symptoms with tribal knowledge from decades of CNC machine and heavy equipment repairs to identify root cause faster than manual diagnostics.
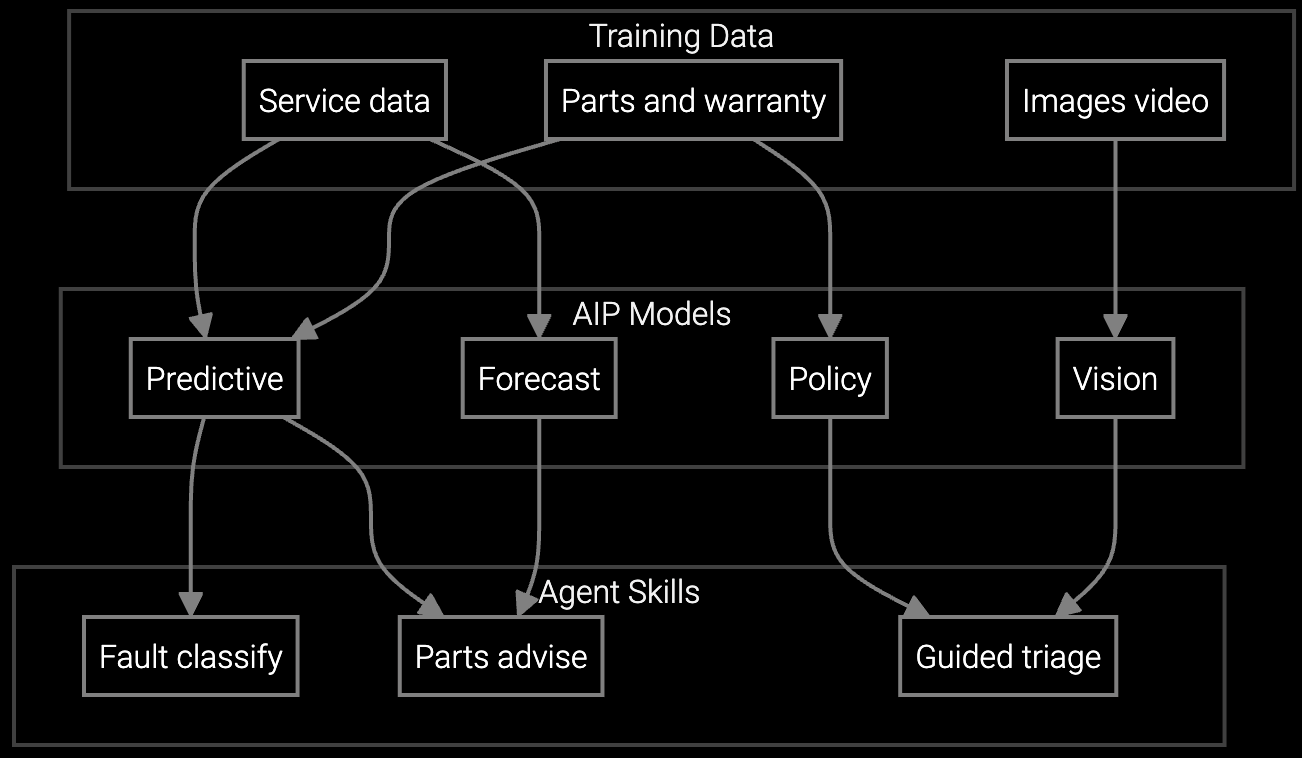
Mobile copilot delivers real-time repair procedures, diagnostic recommendations, and parts identification for legacy industrial machinery—preserving expertise from retiring engineers.
Industrial OEMs support machinery with 15-30 year service obligations where equipment deployed in the 1990s still operates under contract. Documentation for older CNC machines, compressors, and turbines is often incomplete or outdated. Geographic dispersion compounds the challenge—a single OEM may support pumps across mining sites, manufacturing plants, and remote installations worldwide.
The platform ingests PLC telemetry, SCADA data, and condition-monitoring sensors to build predictive models for equipment spanning decades. AI correlates vibration signatures, temperature anomalies, and run-hour data with historical failure patterns to predict breakdowns before they trigger SLA penalties. For legacy equipment lacking sensors, the system learns from repair history and technician notes to guide diagnostics and parts recommendations.
The platform learns from historical repair data, technician notes, and sensor telemetry across the installed base—even for legacy machinery predating modern IoT. AI correlates failure symptoms with past resolutions to guide diagnostics and parts recommendations, preserving institutional knowledge as senior technicians retire.
The platform connects via REST APIs to FSM, ERP, and parts inventory systems. Work order creation, technician scheduling, and parts allocation workflows integrate bidirectionally so dispatch automation and job documentation updates flow seamlessly without rip-and-replace of existing tools.
OEMs typically observe FTF improvement within 90 days as AI begins predicting parts needs and routing optimal expertise. Full workflow automation—including auto-documentation and digital twin updates—scales over six months as the system learns equipment-specific failure patterns.
Yes. The platform captures expertise through structured interviews, repair history analysis, and observation of diagnostic decision patterns. Senior technicians validate AI recommendations during a knowledge transfer phase, encoding decades of experience into models that guide junior technicians on complex legacy equipment repairs.
The system ingests PLC data, SCADA telemetry, condition-monitoring sensors, work order history, parts consumption records, warranty claims, and equipment configuration data. For older machinery lacking sensors, the AI learns from repair notes and failure codes to build predictive models over time.

How AI bridges the knowledge gap as experienced technicians retire.

Generative AI solutions for preserving institutional knowledge.

AI-powered parts prediction for higher FTFR.
See how AI workflow automation reduces truck roll costs and preserves retiring technician expertise.
Schedule Executive Briefing