Repeat truck rolls to CNC machines and turbines drain margins while senior technician expertise walks out the door.
Low first-time fix rates stem from incomplete pre-dispatch diagnostics, missing parts predictions, and lost tribal knowledge. AI-driven root cause analysis, parts forecasting, and mobile decision support reduce repeat visits by surfacing failure patterns and technician expertise in real-time.
Dispatchers lack sensor data context and equipment history. Technicians arrive on-site without knowing the root cause, leading to exploratory visits that waste time and erode customer trust.
Parts prediction relies on manual guesswork from work order descriptions. Technicians discover they need different components only after opening the equipment, forcing a return visit with correct inventory.
Senior technicians retire with decades of troubleshooting heuristics locked in their heads. Junior techs lack context for edge cases on legacy pumps and compressors, extending mean time to repair.
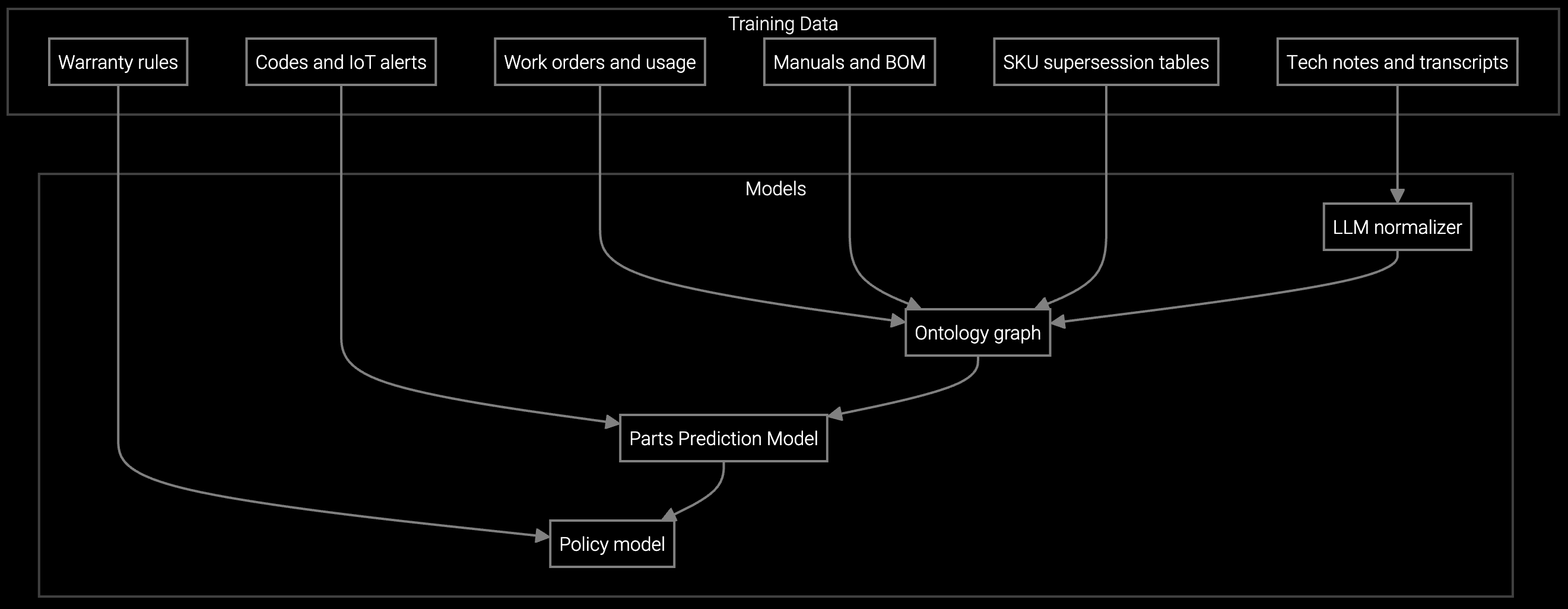
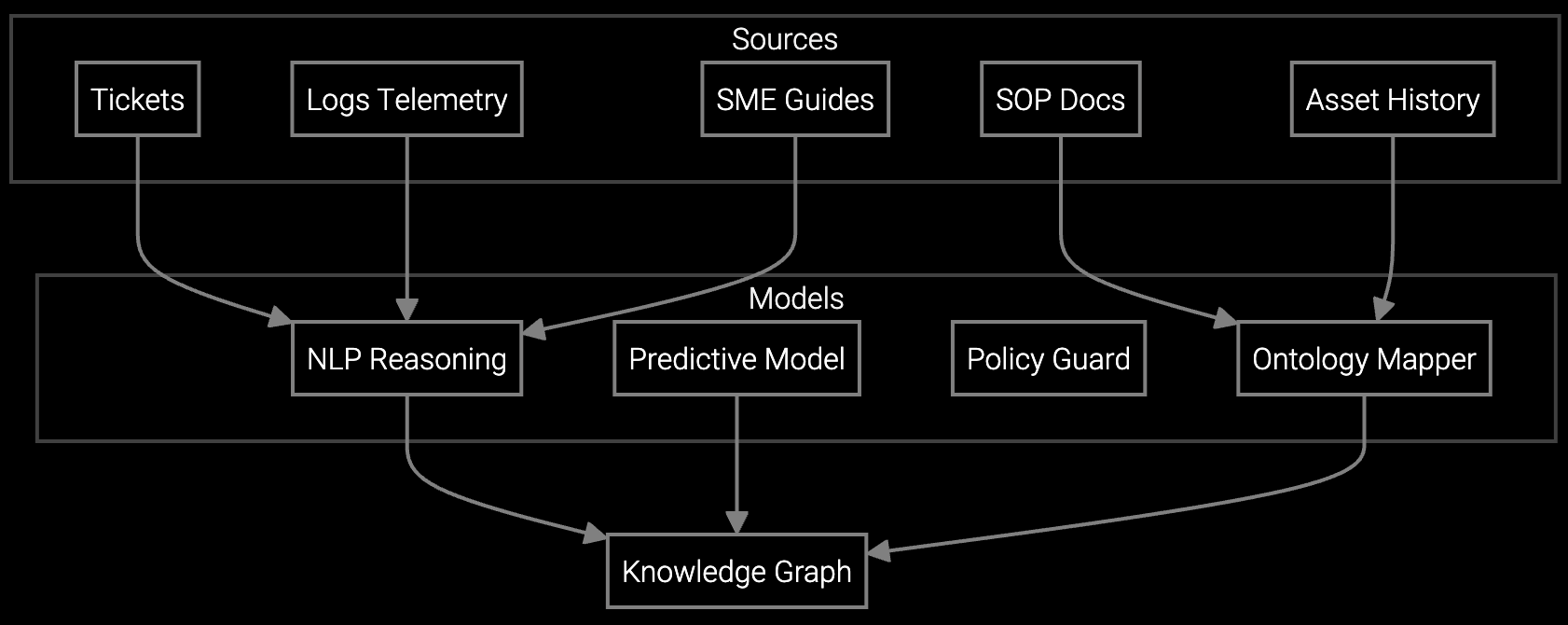
Bruviti's headless platform ingests PLC, SCADA, and IoT sensor telemetry via Python SDKs to build failure pattern libraries. The root cause analysis engine correlates symptom clusters with historical repair outcomes, equipment age, and operating conditions. Parts prediction models train on bill-of-materials data and past consumption patterns, outputting confidence-scored recommendations before dispatch.
Mobile SDKs deliver decision support directly to technician apps, surfacing contextual repair procedures and diagnostic flowcharts without requiring custom UI development. The architecture supports hybrid deployment with on-premise model inference for air-gapped factory environments and cloud-based retraining pipelines. Open APIs enable FSM integration without vendor lock-in, preserving flexibility to swap downstream tools.
Predicts bearings, seals, and motor components for CNC machines and turbines before dispatch, reducing truck rolls for missing inventory by 67%.
Correlates vibration anomalies and pressure spikes with historical pump failure modes, surfacing probable root cause before technician leaves the warehouse.
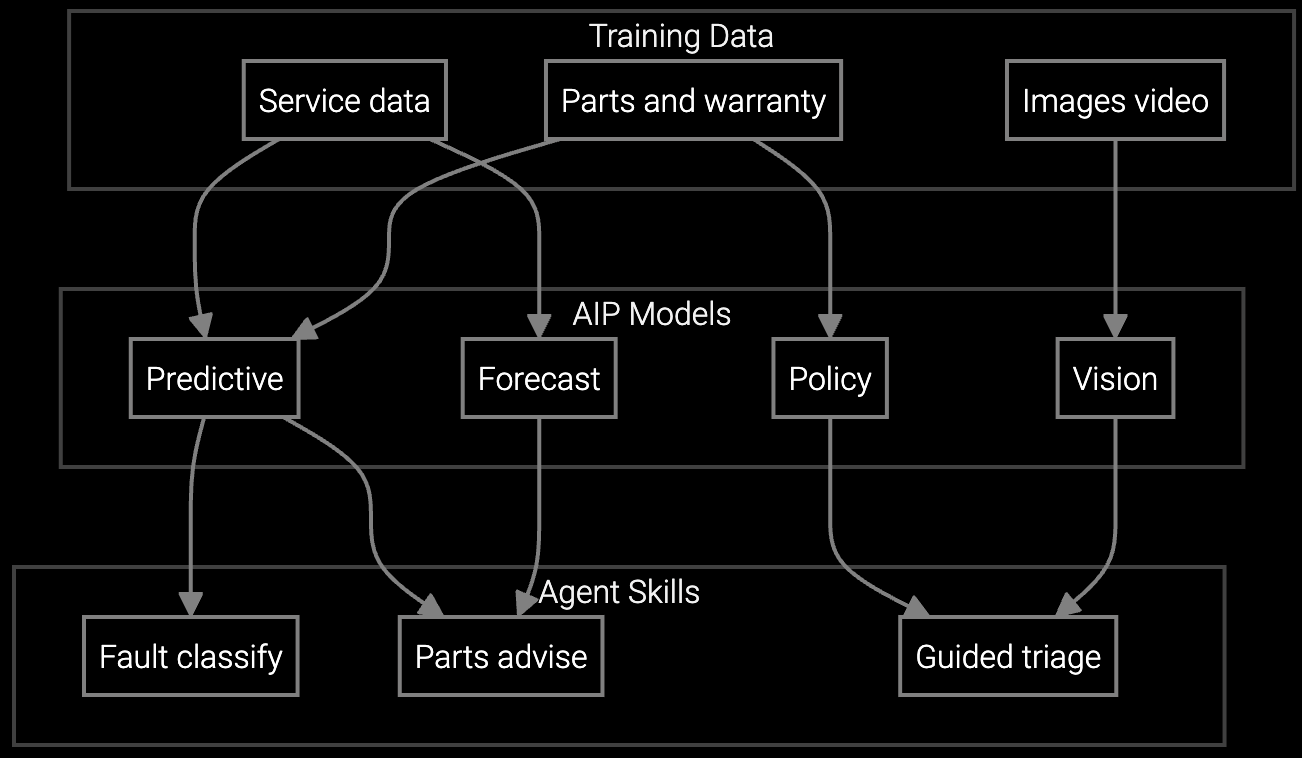
Mobile copilot delivers alignment procedures and hydraulic troubleshooting steps on-site, replacing 500-page manuals with contextual guidance keyed to equipment serial number and installed options.
Industrial machinery operates for 15-30 years with evolving configurations and undocumented modifications. Technicians face CNC machines with controller upgrades, retrofitted sensors, and custom tooling that diverge from original blueprints. Root cause identification depends on correlating decades of repair history with current sensor baselines, a task that overwhelms manual lookup.
Parts obsolescence compounds the problem. Original components become unavailable, requiring cross-reference to substitutes with different failure modes. Tribal knowledge of which aftermarket bearings fit which machine generations lives only in senior technician memory, making first-time fix impossible when they retire.
The platform flags low-confidence predictions and surfaces similar historical cases for technician review. You can retrain models incrementally as new failure modes appear, without waiting for batch retraining cycles. Uncertainty quantification prevents false positives that would erode trust.
Parts prediction models train on work order history, bill-of-materials structures, equipment age, and sensor telemetry if available. Minimum viable dataset requires 12-18 months of consumption records. The Python SDK includes data loaders for SAP ECC, Oracle EBS, and custom CSV exports.
Yes. Bruviti supports hybrid deployment where inference runs on local GPUs behind the firewall while model updates sync via secure transfer during maintenance windows. This preserves data sovereignty for manufacturers with IP protection requirements while enabling continuous improvement.
Structured interviews convert heuristics into decision trees that feed model training. Technicians annotate historical repair cases with contextual notes that become training labels. The mobile SDK records resolution steps and outcomes to build a corpus of expert reasoning patterns that junior techs can query in real-time.
REST APIs expose root cause scores, parts recommendations, and knowledge retrieval endpoints that FSM platforms consume via webhook or polling. SDKs for Python and TypeScript accelerate custom integrations. Open standards like OpenAPI ensure you avoid vendor lock-in if requirements change.

How AI bridges the knowledge gap as experienced technicians retire.

Generative AI solutions for preserving institutional knowledge.

AI-powered parts prediction for higher FTFR.
Explore Bruviti's Python SDKs and open APIs for industrial equipment field service.
Schedule Technical Demo